Unveiling The Secrets Of The Food Chain In The Desert Biome
Hey there, nature enthusiasts! Today, we’re diving deep into one of the most fascinating ecosystems on our planet—the desert biome. Now, let me ask you this: have you ever wondered how life thrives in such an extreme environment? Well, it all comes down to the food chain of the desert biome. This intricate web of life is what keeps everything in balance, and trust me, it’s more interesting than you might think.
The food chain in the desert biome is like a well-oiled machine. Each organism plays a crucial role, ensuring that energy flows smoothly from one level to the next. From tiny plants to apex predators, every living thing contributes to this delicate ecosystem. So, if you’re ready to explore the hidden wonders of the desert’s food chain, stick around because we’ve got some incredible facts to share.
But before we dive in, let’s set the stage. The desert biome is not just a barren wasteland. It’s home to a diverse range of species that have adapted to survive in harsh conditions. These adaptations are what make the desert food chain so unique and worth studying. Ready to learn more? Let’s get started!
- Lo Bosworth Married The Inside Scoop You Didnrsquot Know You Needed
- Bad Things About Aquarius The Truth Behind The Water Bearers Flaws
What Exactly is the Desert Biome?
Alright, let’s break it down. The desert biome is an ecosystem characterized by extremely low precipitation and high temperatures. But don’t be fooled by its arid appearance; it’s teeming with life. From the scorching Sahara to the rugged Mojave, deserts cover about one-third of Earth’s land surface. And guess what? Each desert has its own unique food chain that supports a variety of species.
Deserts may look barren, but they’re actually full of surprises. Plants like cacti and shrubs have developed special ways to store water, while animals have evolved to thrive in the heat. These adaptations are key to understanding how the food chain works in such an unforgiving environment. So, let’s take a closer look at the players in this ecological drama.
Producers: The Foundation of the Desert Food Chain
At the base of every food chain are the producers, and in the desert, these are the plants that manage to survive despite the lack of water. Cacti, succulents, and drought-resistant grasses are just a few examples of these hardy organisms. They use photosynthesis to convert sunlight into energy, which then becomes the building block for the entire food chain.
- How To Apply For A Zales Credit Card Your Ultimate Guide
- Marilyn Manson And Sons Of Anarchy A Deep Dive Into The Connection
Here’s a fun fact: some desert plants have spines instead of leaves to reduce water loss. Others have deep root systems to tap into underground water sources. These adaptations make them perfectly suited to their environment and ensure that they can continue to provide energy for the rest of the ecosystem.
Key Desert Plants
- Saguaro Cactus
- Joshua Tree
- Creosote Bush
- Desert Ironwood
These plants are the backbone of the desert food chain, providing food and shelter for countless animals. Without them, the entire ecosystem would collapse. So, let’s give a round of applause to these unsung heroes of the desert!
Primary Consumers: The Herbivores of the Desert
Next up, we have the primary consumers, or herbivores, who feed directly on the producers. These animals range from small insects to larger mammals, all of whom have adapted to the desert’s harsh conditions. Some common herbivores in the desert include jackrabbits, kangaroo rats, and various species of insects.
Now, here’s where things get interesting. Many desert herbivores have developed unique ways to conserve water. For example, kangaroo rats can survive without ever drinking water, getting all the moisture they need from the seeds they eat. That’s pretty impressive, right?
Adaptations of Desert Herbivores
- Nocturnal behavior to avoid the heat
- Water-efficient kidneys
- Specialized diets to maximize nutrient intake
These adaptations allow herbivores to thrive in an environment where water is scarce. By consuming plants, they transfer energy to the next level of the food chain, paving the way for the predators.
Secondary Consumers: The Carnivores of the Desert
Alright, let’s talk about the meat-eaters. Secondary consumers, or carnivores, play a crucial role in maintaining balance in the desert food chain. These predators feed on herbivores, controlling their populations and ensuring that no single species dominates the ecosystem.
Some of the most iconic desert carnivores include coyotes, snakes, and hawks. Each of these animals has its own unique hunting strategies and adaptations. For instance, sidewinder snakes move in a zigzag pattern to minimize contact with the hot sand, while hawks use their keen eyesight to spot prey from great distances.
Top Desert Predators
- Coyotes
- Sidewinder Snakes
- Red-Tailed Hawks
- Bobcats
These predators are the ultimate survivors, using their skills and adaptations to thrive in one of the harshest environments on Earth. Without them, the desert food chain would quickly fall out of balance.
Decomposers: The Unsung Heroes of the Desert
Every food chain needs decomposers, and the desert is no exception. These organisms break down dead plant and animal matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. In the desert, decomposers include fungi, bacteria, and various types of insects.
Even in such a dry environment, decomposers manage to thrive. They play a vital role in maintaining the health of the ecosystem by ensuring that nutrients are continuously cycled through the food chain. Without them, the desert would quickly become a wasteland.
Importance of Decomposers
- Recycling nutrients
- Breaking down organic matter
- Supporting plant growth
So, next time you see a scorpion or a beetle in the desert, remember that they’re doing their part to keep the ecosystem healthy. These little creatures are the unsung heroes of the desert food chain.
Energy Flow in the Desert Food Chain
Now that we’ve covered the players, let’s talk about how energy flows through the desert food chain. It all starts with the sun, which provides the energy that plants use for photosynthesis. This energy is then passed on to herbivores when they eat the plants, and from there, it moves up the chain to carnivores.
But here’s the thing: energy transfer is not 100% efficient. At each level of the food chain, some energy is lost as heat. This is why there are usually more producers than consumers and more herbivores than carnivores. It’s all about maintaining balance in the ecosystem.
Energy Pyramid
- Producers: Largest population
- Herbivores: Smaller population
- Carnivores: Smallest population
This pyramid structure ensures that energy is distributed efficiently throughout the ecosystem. It’s a delicate balance that has evolved over millions of years, and it’s what makes the desert food chain so fascinating.
Threats to the Desert Food Chain
Unfortunately, like many ecosystems, the desert food chain is under threat. Climate change, habitat destruction, and human activities are all taking their toll on this delicate balance. Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns are affecting the availability of water, which is crucial for the survival of desert plants and animals.
In addition, invasive species are disrupting the natural order of the food chain. These non-native species can outcompete native organisms for resources, leading to a decline in biodiversity. It’s a serious issue that requires immediate attention if we want to preserve the desert biome for future generations.
Conservation Efforts
- Protecting natural habitats
- Controlling invasive species
- Reducing human impact
By taking action now, we can help ensure that the desert food chain remains healthy and vibrant. It’s up to all of us to do our part in protecting this incredible ecosystem.
Fun Facts About the Desert Food Chain
Before we wrap up, let’s take a look at some fun facts about the desert food chain. Did you know that:
- The Gila monster is one of the few venomous lizards in the world?
- The horned lizard can squirt blood from its eyes to deter predators?
- Desert tortoises can live for over 80 years?
These are just a few examples of the incredible diversity found in the desert biome. Each species has its own unique story, and together, they form a complex and fascinating food chain.
Conclusion
So, there you have it—a deep dive into the food chain of the desert biome. From the hardy producers to the fierce predators, every organism plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of this incredible ecosystem. By understanding how the food chain works, we can better appreciate the complexity and beauty of life in the desert.
Now, it’s your turn. Leave a comment below and let us know what you think. Did you learn something new? Do you have any questions? And don’t forget to share this article with your friends and family. Together, we can spread awareness about the importance of preserving our planet’s diverse ecosystems.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is the Desert Biome?
- Producers: The Foundation of the Desert Food Chain
- Primary Consumers: The Herbivores of the Desert
- Secondary Consumers: The Carnivores of the Desert
- Decomposers: The Unsung Heroes of the Desert
- Energy Flow in the Desert Food Chain
- Threats to the Desert Food Chain
- Fun Facts About the Desert Food Chain
- Conclusion
- What Is Mma Fighter Unveiling The World Of Ultimate Warriors
- Cancel Progressive Auto Insurance A Straightforward Guide To Unhooking Without The Drama
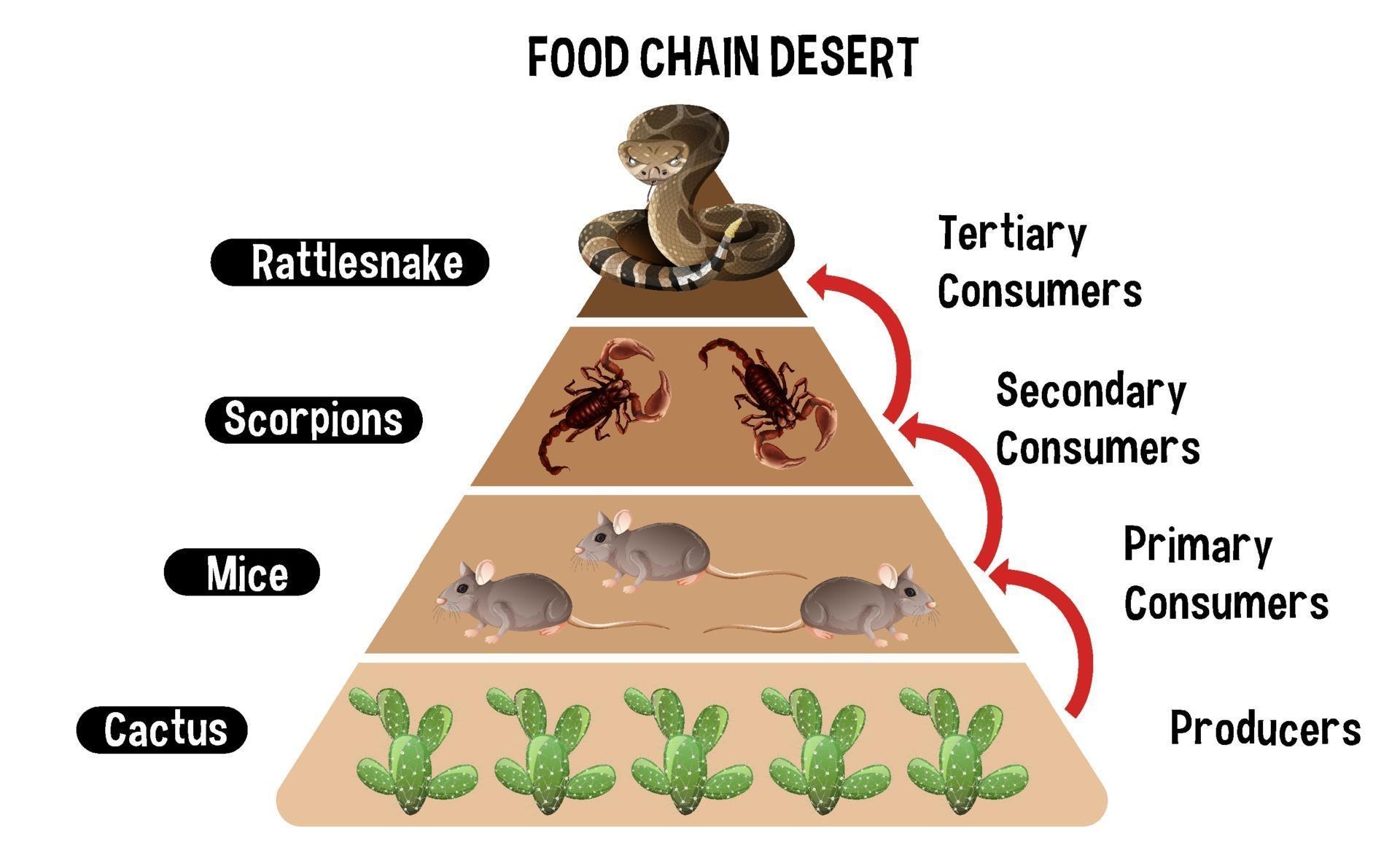
Diagram showing Desert food chain for education 2379595 Vector Art at
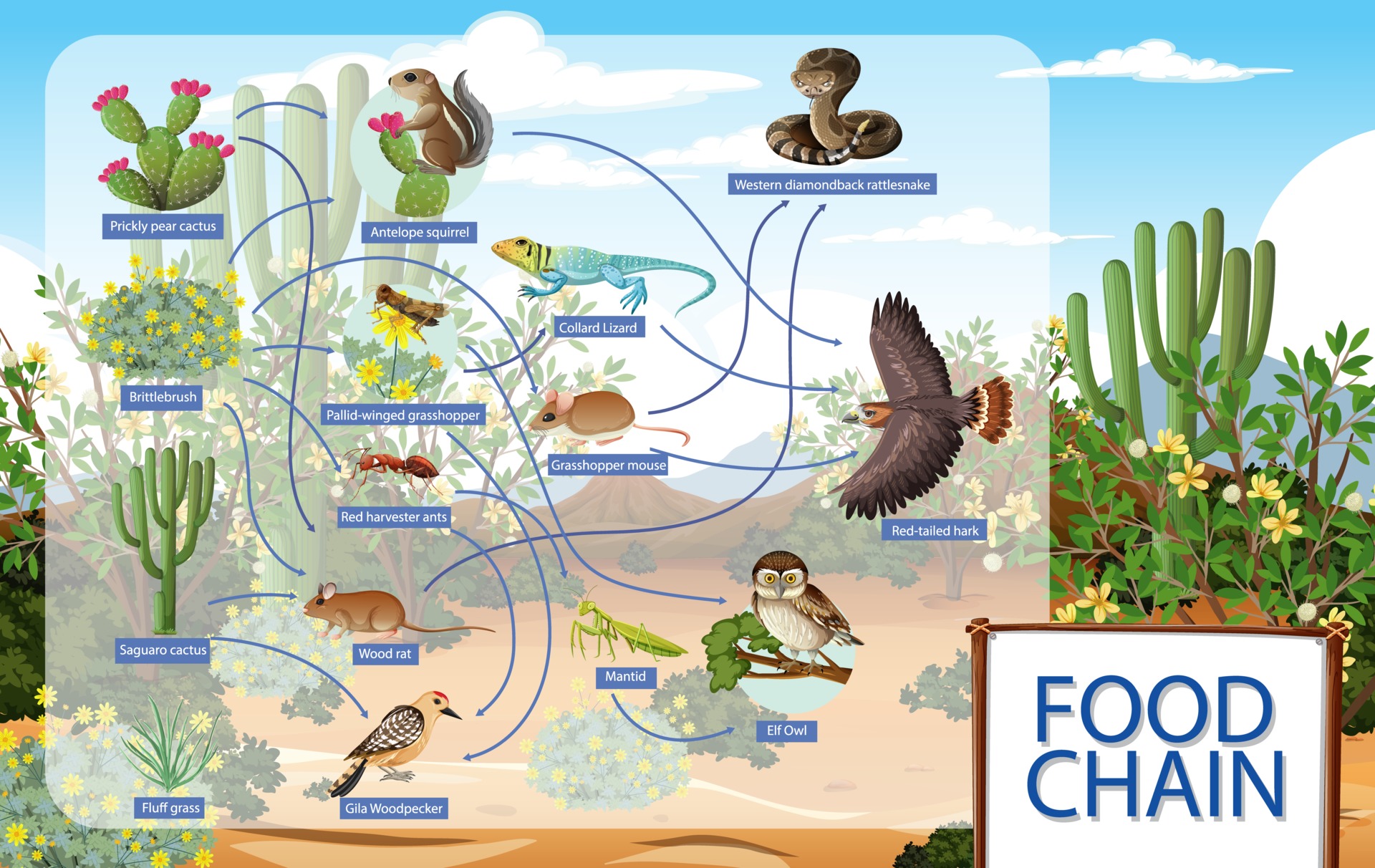
Diagram showing desert animals food chain 2952865 Vector Art at Vecteezy
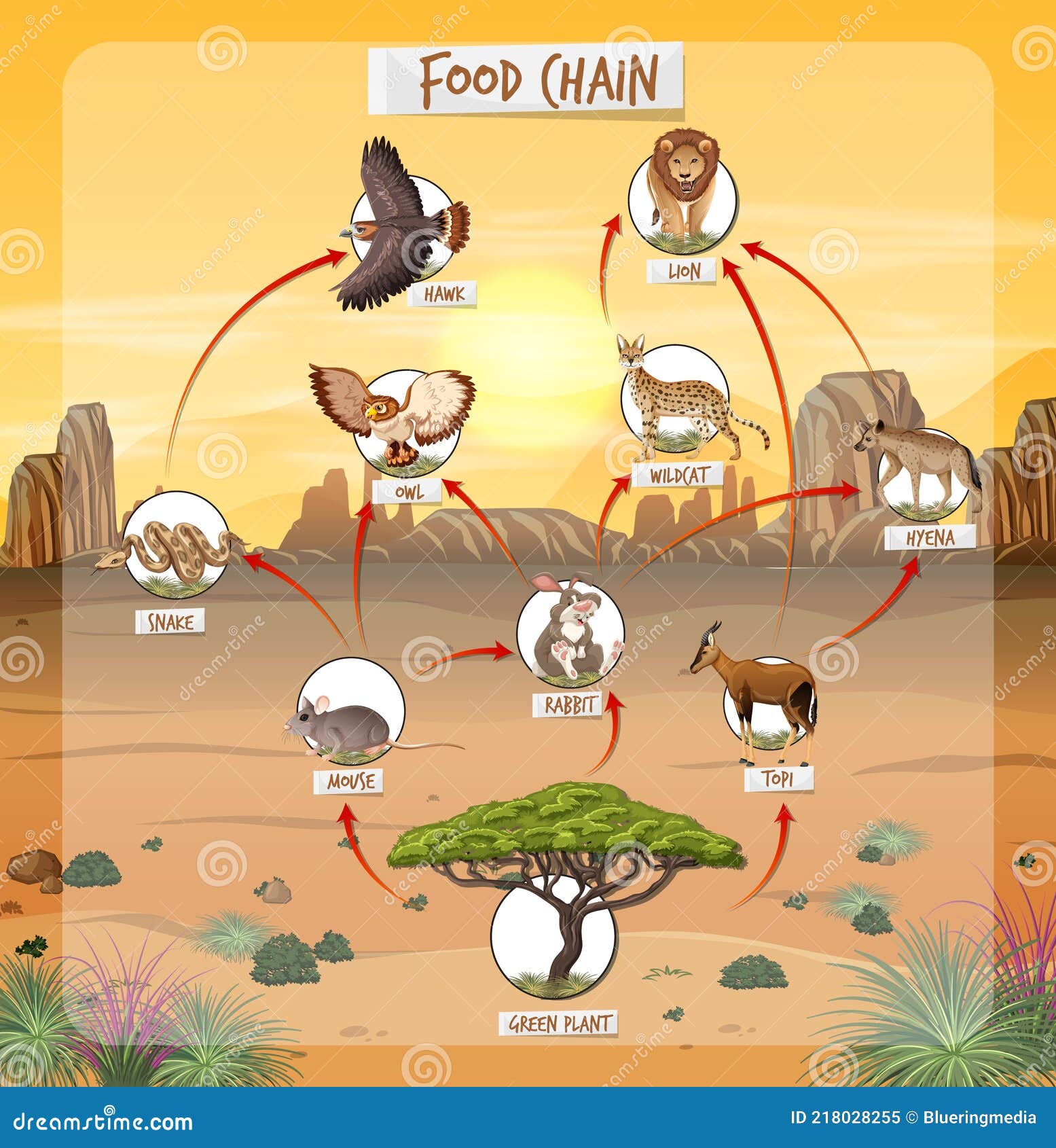
Sahara Desert Food Chain