Unlock The Secrets Of Desert Food Web: A Fascinating Journey Through Nature's Balance
Hey there, nature lovers! If you're into ecosystems and how everything in the wild is interconnected, you're about to dive into something truly amazing. The desert food web is a complex yet fascinating topic that sheds light on how life thrives in some of the harshest environments on the planet. Let's get started, shall we? This ain't just about sand and cacti; it's about survival, adaptation, and the delicate balance of life in the desert.
You might be thinking, "How can anything survive in a place where water is as rare as a unicorn sighting?" Well, buckle up, because the desert food web is a masterclass in resourcefulness. It's not just about who eats whom; it's about how every living thing, from the tiniest insect to the largest predator, plays a crucial role in maintaining the ecosystem. So, whether you're a biology buff or just curious about nature, this is gonna blow your mind.
Now, before we dive deeper, let me tell you why understanding the desert food web matters. It's not just about appreciating the desert; it's about learning how ecosystems function and how human actions can impact these delicate balances. Ready to explore? Let's go!
- Discovering The Charm Of Chapel Hill A Unique College Town Experience
- Who Is Melanie Martinez Dating In 2024 The Ultimate Guide To Her Love Life And More
What Exactly is a Desert Food Web?
Alright, let's break it down. A desert food web is basically a map of who eats whom in the desert ecosystem. Think of it like a giant puzzle where every piece has a role. It starts with the producers—plants that can survive in the desert—and goes all the way up to the apex predators. But here's the twist: it's not a straight line. It's a web, meaning there are multiple connections and interactions that keep the whole system in check.
Key Components of the Desert Food Web
Let's talk about the main players in this desert drama. First up, we've got the producers. These are the plants that manage to survive in the scorching heat and minimal water. Then, there are the primary consumers—herbivores that munch on these plants. Next, we have the secondary consumers—carnivores that eat the herbivores. Finally, there are the apex predators, the big bosses of the desert food chain.
Here's a quick rundown of the main components:
- Who Does Martha Stewart Support Politically In 2024 A Deep Dive
- How Much Is Stallone Worth Discover The Net Worth Of A Hollywood Legend
- Producers: Plants like cacti and shrubs that can store water.
- Primary Consumers: Insects, rodents, and small mammals that eat plants.
- Secondary Consumers: Reptiles, birds, and small predators that feed on primary consumers.
- Apex Predators: Large predators like snakes and coyotes that sit at the top of the food web.
Understanding the Role of Producers in the Desert Food Web
Plants are the unsung heroes of the desert. Without them, the whole food web would collapse. These producers are specially adapted to survive in extreme conditions. They have thick skins to prevent water loss, deep roots to tap into underground water sources, and spines instead of leaves to reduce water evaporation. Some even have the ability to go dormant during dry spells and spring back to life when it rains.
Types of Desert Plants
So, what kind of plants are we talking about here? Let's take a look at some of the most common desert producers:
- Cacti: These spiky guys are masters of water conservation.
- Succulents: Like cacti, they store water in their leaves.
- Shrubs: Hardy plants that can survive on minimal water.
- Grasses: Some grasses have adapted to desert life by growing deep roots.
Primary Consumers: The Desert's Little Eaters
Now, let's talk about the primary consumers. These are the animals that munch on the desert plants. They range from tiny insects to larger mammals. One of the coolest things about these creatures is their ability to survive on such a limited diet. They've developed some pretty neat tricks to get the most out of their food.
Examples of Primary Consumers
Here are some examples of primary consumers in the desert:
- Insects: Like beetles and ants that feed on plant sap.
- Rodents: Such as kangaroo rats that eat seeds and plant material.
- Small Mammals: Like rabbits that graze on desert grasses.
Secondary Consumers: The Desert's Carnivores
Next up, we've got the secondary consumers. These are the predators that feed on the primary consumers. They're a bit higher up the food web, but they're still not at the top. These animals are usually faster and more agile than their prey, which helps them catch their meals.
Types of Secondary Consumers
Here are some examples of secondary consumers:
- Reptiles: Like lizards that eat insects.
- Birds: Such as roadrunners that hunt small mammals.
- Small Predators: Like foxes that prey on rodents.
Apex Predators: The Kings of the Desert
Finally, we reach the top of the food web—the apex predators. These are the big guys that don't have any natural predators. They're the ones that keep the population of secondary consumers in check. Without them, the whole food web could become unbalanced.
Examples of Apex Predators
Here are some examples of apex predators in the desert:
- Snakes: Like rattlesnakes that hunt small mammals.
- Coyotes: These clever canines are expert hunters.
- Birds of Prey: Such as hawks that soar above the desert hunting for prey.
The Delicate Balance of the Desert Food Web
Now that we've met all the players, let's talk about why this balance is so important. Every organism in the desert food web depends on the others to survive. If one link in the chain is disrupted, it can have a ripple effect throughout the entire ecosystem. For example, if a disease wipes out a certain type of plant, the herbivores that eat those plants will struggle to survive, which in turn affects the predators that eat those herbivores.
Factors That Affect the Desert Food Web
Here are some factors that can impact the desert food web:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures can make it even harder for desert organisms to survive.
- Habitat Loss: Human activities like mining and urban development can destroy desert habitats.
- Introduced Species: Non-native species can disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystem.
Why Should We Care About the Desert Food Web?
Alright, so you might be wondering why we should care about what happens in the desert. The truth is, everything in nature is connected. What happens in the desert can have far-reaching effects on other ecosystems. Plus, understanding the desert food web can help us learn more about how ecosystems function in general. It's like a microcosm of the bigger picture.
Conservation Efforts
There are lots of efforts underway to protect desert ecosystems and the food webs that depend on them. These include:
- Protected Areas: Designating certain areas as nature reserves to prevent human interference.
- Research: Studying desert ecosystems to better understand how they work.
- Education: Teaching people about the importance of desert conservation.
Conclusion: The Wonders of the Desert Food Web
So, there you have it—the incredible world of the desert food web. From the tiniest insect to the largest predator, every organism plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of this unique ecosystem. Understanding how the desert food web works not only helps us appreciate the beauty of nature but also reminds us of our responsibility to protect it.
Now, here's the thing: the desert food web is more than just a science lesson. It's a reminder of how interconnected everything in nature is. So, the next time you see a cactus or a snake, take a moment to appreciate the complex web of life that allows them to thrive in such a harsh environment. And who knows? You might just learn something new about the world around you.
So, what do you think? Are you ready to explore the desert food web further? Drop a comment below or share this article with your friends. Let's keep the conversation going and spread the word about the wonders of nature!
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is a Desert Food Web?
- Key Components of the Desert Food Web
- Understanding the Role of Producers in the Desert Food Web
- Primary Consumers: The Desert's Little Eaters
- Secondary Consumers: The Desert's Carnivores
- Apex Predators: The Kings of the Desert
- The Delicate Balance of the Desert Food Web
- Factors That Affect the Desert Food Web
- Why Should We Care About the Desert Food Web?
- Conservation Efforts
- How Far From Alaska To Russia A Fascinating Journey Across Continents
- Club America The Heartbeat Of Mexican Soccer
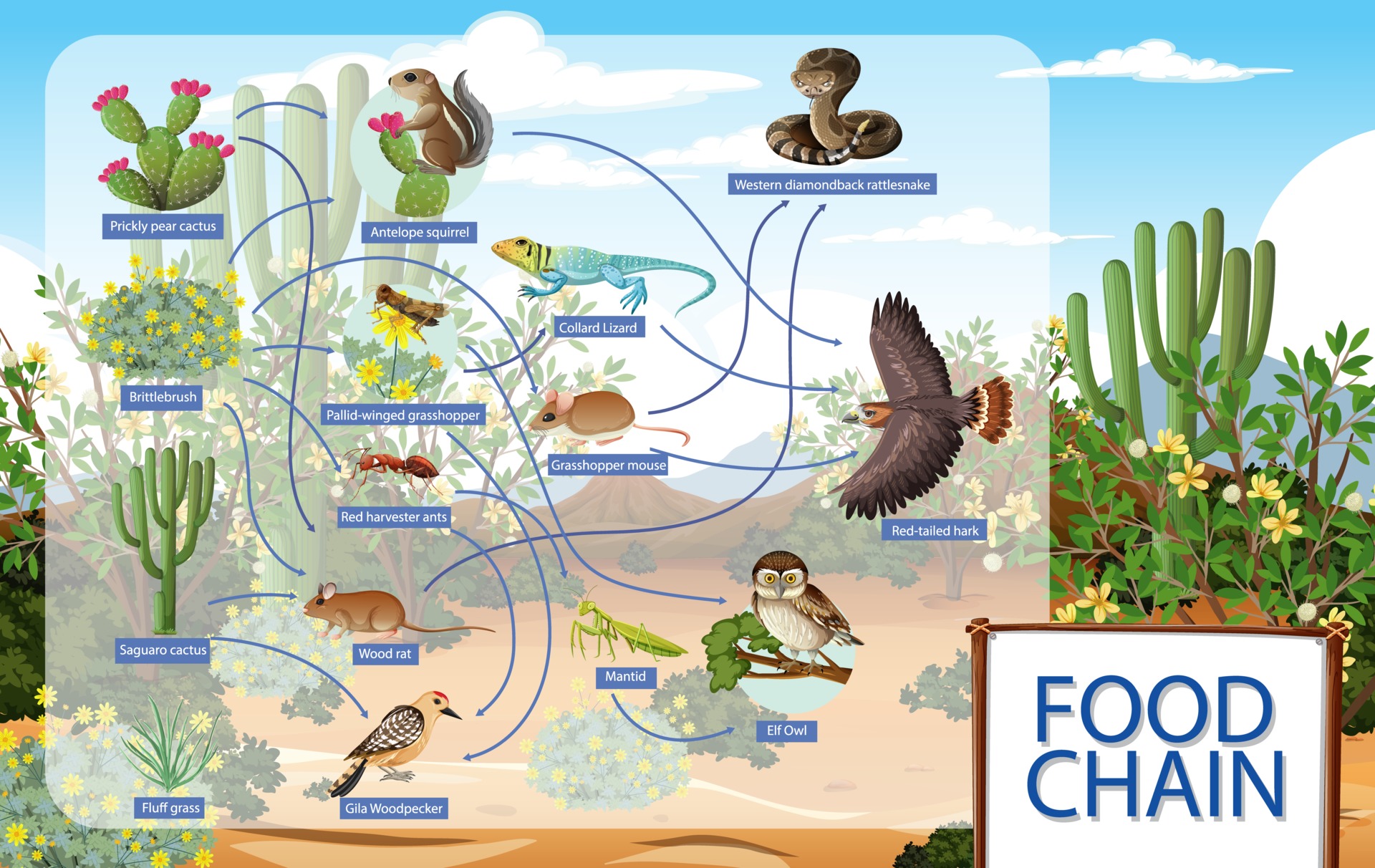
Diagram showing desert animals food chain 2952865 Vector Art at Vecteezy
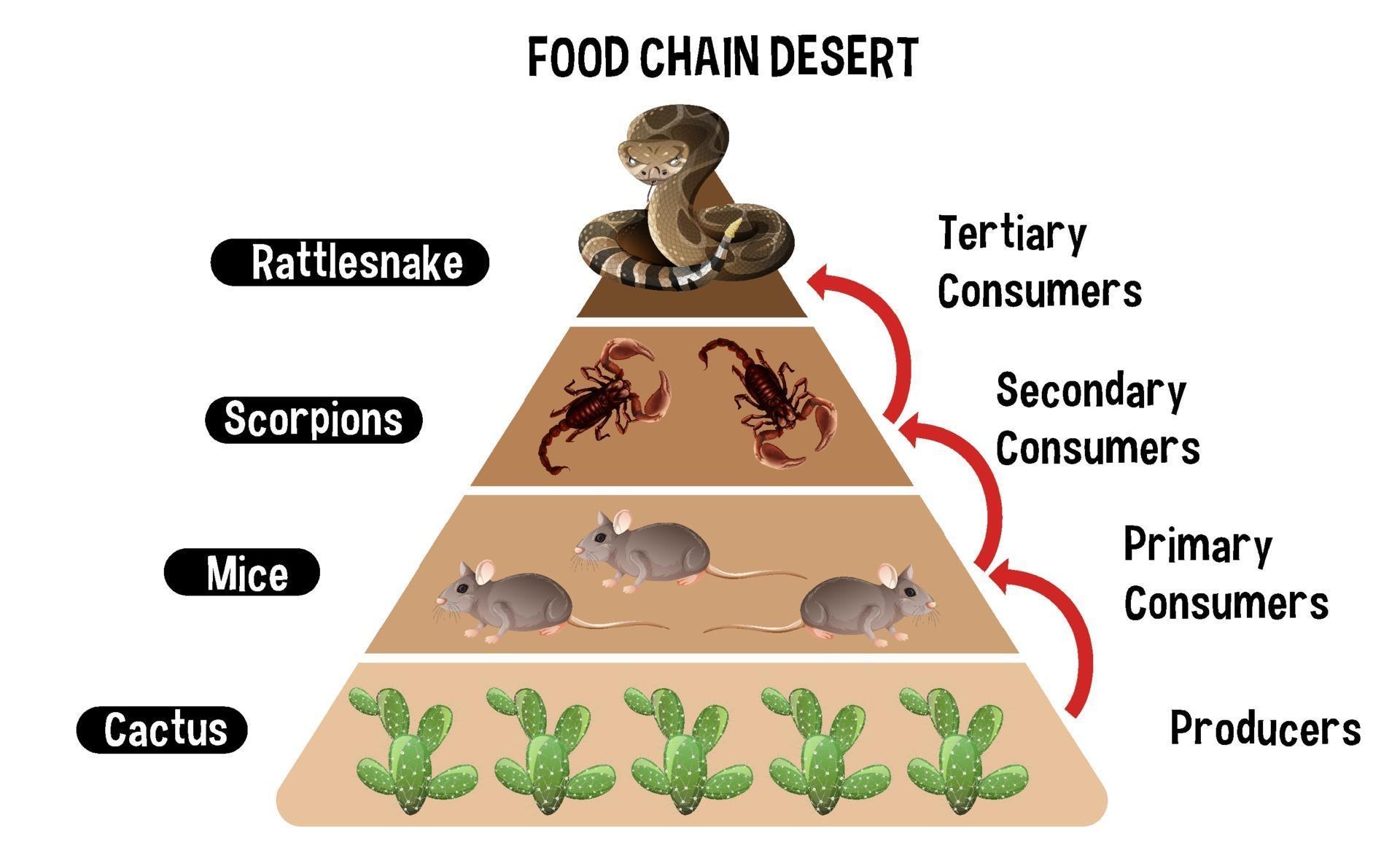
Diagram showing Desert food chain for education 2379595 Vector Art at

Sonoran Desert food web